- Korea, South
-
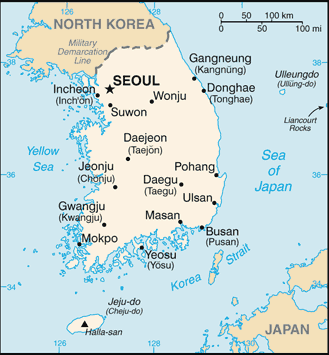 Introduction ::Korea, SouthBackground:An independent kingdom for much of its long history, Korea was occupied by Japan beginning in 1905 following the Russo-Japanese War. In 1910, Tokyo formally annexed the entire Peninsula. Korea regained its independence following Japan's surrender to the United States in 1945. After World War II, a democratic-based government (Republic of Korea, ROK) was set up in the southern half of the Korean Peninsula while a communist-style government was installed in the north (Democratic People's Republic of Korea, DPRK). During the Korean War (1950-53), US troops and UN forces fought alongside ROK soldiers to defend South Korea from a DPRK invasion supported by China and the Soviet Union. A 1953 armistice split the peninsula along a demilitarized zone at about the 38th parallel. PARK Chung-hee took over leadership of the country in a 1961 coup. During his regime, from 1961 to 1979, South Korea achieved rapid economic growth, with per capita income rising to roughly 17 times the level of North Korea. South Korea held its first free presidential election under a revised democratic constitution in 1987, with former ROK Army general ROH Tae-woo winning a close race. In 1993, KIM Young-sam (1993-98) became South Korea's first civilian president. South Korea today is a fully functioning modern democracy. LEE Myung-bak (2008-2013) pursued a policy of global engagement , highlighted by Seoul's hosting of the G-20 summit in November 2010 and the Nuclear Security Summit in March 2012. South Korea also secured a non-permanent seat (2013-14) on the UN Security Council and will host the 2018 Winter Olympic Games. President PARK Geun-hye took office in February 2013 and is South Korea's first female leader. Serious tensions with North Korea have punctuated inter-Korean relations in recent years, including the North's sinking of the South Korean warship Cheonan in March 2010 and its artillery attack on South Korean soldiers and citizens in November 2010. In January 2013, South Korea assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2013-14 term.Geography ::Korea, SouthLocation:Eastern Asia, southern half of the Korean Peninsula bordering the Sea of Japan and the Yellow SeaGeographic coordinates:37 00 N, 127 30 EArea:total: 99,720 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 109land: 96,920 sq kmwater: 2,800 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than IndianaLand boundaries:total: 238 kmborder countries: North Korea 238 kmCoastline:2,413 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nm; between 3 nm and 12 nm in the Korea Straitcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: not specifiedClimate:temperate, with rainfall heavier in summer than winterTerrain:mostly hills and mountains; wide coastal plains in west and southElevation extremes:lowest point: Sea of Japan 0 mhighest point: Halla-san 1,950 mNatural resources:coal, tungsten, graphite, molybdenum, lead, hydropower potentialLand use:arable land: 14.93%permanent crops: 2.06%other: 83% (2011)Irrigated land:8,804 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:69.7 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 25.47 cu km/yr (26%/12%/62%)per capita: 548.7 cu m/yr (2003)Natural hazards:occasional typhoons bring high winds and floods; low-level seismic activity common in southwestvolcanism: Halla (elev. 1,950 m) is considered historically active although it has not erupted in many centuriesEnvironment - current issues:air pollution in large cities; acid rain; water pollution from the discharge of sewage and industrial effluents; drift net fishingEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:strategic location on Korea StraitPeople and Society ::Korea, SouthNationality:noun: Korean(s)adjective: KoreanEthnic groups:homogeneous (except for about 20,000 Chinese)Languages:Korean, English (widely taught in junior high and high school)Religions:Christian 31.6% (Protestant 24%, Roman Catholic 7.6%), Buddhist 24.2%, other or unknown 0.9%, none 43.3% (2010 survey)Population:48,955,203 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Age structure:0-14 years: 14.6% (male 3,717,701/female 3,424,490)15-24 years: 13.6% (male 3,525,050/female 3,117,198)25-54 years: 47.8% (male 11,925,181/female 11,491,841)55-64 years: 11.7% (male 2,842,996/female 2,907,730)65 years and over: 12.3% (male 2,469,093/female 3,533,923) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 37.1 %youth dependency ratio: 20.4 %elderly dependency ratio: 16.7 %potential support ratio: 6 (2013)Median age:total: 39.7 yearsmale: 38.2 yearsfemale: 41 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.18% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Birth rate:8.33 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 219Death rate:6.5 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Net migration rate:0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Urbanization:urban population: 83.2% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 0.71% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:SEOUL (capital) 9.778 million; Busan (Pusan) 3.439 million; Incheon (Inch'on) 2.572 million; Daegu (Taegu) 2.458 million; Daejon (Taejon) 1.497 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.09 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.13 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.04 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.69 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:29.6 (2008 est.)Maternal mortality rate:16 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 144Infant mortality rate:total: 4.01 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 200male: 4.21 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.79 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 79.55 yearscountry comparison to the world: 42male: 76.4 yearsfemale: 82.91 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.24 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 219Contraceptive prevalence rate:80%note: percent of women aged 15-44 (2009)Health expenditures:6.9% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 85Physicians density:1.97 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:10.3 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 88% of populationtotal: 98% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 12% of populationtotal: 2% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 142HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:9,500 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 100HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 500 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 85Obesity - adult prevalence rate:7.7% (2008)country comparison to the world: 139Education expenditures:5.1% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 74Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 97.9%male: 99.2%female: 96.6% (2002)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 yearsmale: 18 yearsfemale: 16 years (2010)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 9.6%country comparison to the world: 108male: 12.1%female: 8.1% (2011)Government ::Korea, SouthCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Koreaconventional short form: South Korealocal long form: Taehan-min'guklocal short form: Han'gukabbreviation: ROKGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Seoulgeographic coordinates: 37 33 N, 126 59 Etime difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:9 provinces (do, singular and plural), 6 metropolitan cities (gwangyoksi, singular and plural), 1 special city, and 1 special self-governing cityprovinces: Chungbuk (North Chungcheong), Chungnam (South Chungcheong), Gangwon, Gyeonggi, Gyeongbuk (North Gyeongsang), Gyeongnam (South Gyeongsang), Jeju, Jeonbuk (North Jeolla), Jeonnam (South Jeolla)metropolitan cities: Busan (Pusan), Daegu (Taegu), Daejon (Taejon), Gwangju (Kwangju), Incheon (Inch'on), Ulsanspecial city: Seoulspecial self-governing city: SejongIndependence:15 August 1945 (from Japan)National holiday:Liberation Day, 15 August (1945)Constitution:17 July 1948; note - amended or rewritten many times; current constitution approved 29 October 1987Legal system:mixed legal system combining European civil law, Anglo-American law, and Chinese classical thoughtInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:19 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President PARK Geun-hye (since 25 February 2013)head of government: Prime Minister CHUNG Hong-won (since 26 February 2013); Deputy Prime Minister HYUN Oh-seok (since 26 June 2013)cabinet: State Council appointed by the president on the prime minister's recommendation(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a single five-year term; PARK Geun-hye elected on 19 December 2012; next election to be held in December 2017; prime minister appointed by president with consent of National Assemblyelection results: PARK Geun-Hye elected president on 19 December 2012; percent of vote - PARK Geun-Hye (NFP) 51.6%, MOON Jae-In (DUP) 48%, others 0.4%Legislative branch:unicameral National Assembly or Gukhoe (300 seats; 246 members elected in single-seat constituencies, 54 elected by proportional representation; members serve four-year terms)elections: last held on 11 April 2012 (next to be held in April 2016)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NFP 152, DUP 127, UPP 13, LFP 5, independents 3Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of South Korea (consists of a chief justice and 13 justices); Constitutional Court (consists of a court head and 8 justices)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president with the consent of the National Assembly; other justices appointed by the president upon the recommendation of the chief justice and consent of the National Assembly; position of the chief justice is a 6-year non-renewable term; other justices serve 6-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court justices appointed - 3 by the president, 3 by the National Assembly, and 3 by the Supreme Court chief justice; court head serves until retirement at age 70, while other justices serve 6-year renewable terms with mandatory retirement at age 65subordinate courts: High Courts; District Courts; Branch Courts (organized undeer the Branch Courts); specialized courts for family and administrative issuesPolitical parties and leaders:Democratic Party or DP (formerly the Democratic United Party or DUP) [KIM Han-gil]Liberty Forward Party or LFP (now part of the NFP)New Frontier Party (NFP) or Saenuri (formerly Grand National Party) [HWANG Woo-yea]Progressive Justice Party or PJP [ROH Hoe-chan and CHO Joon-ho]United Progressive Party or UPP [LEE Jung-hee]Political pressure groups and leaders:Catholic Priests' Association for JusticeCitizen's Coalition for Economic JusticeFederation of Korean IndustriesFederation of Korean Trade UnionsKorean Confederation of Trade UnionsKorean Veterans' AssociationLawyers for a Democratic SocietyNational Council of ChurchesPeople's Solidarity for Participatory DemocracyInternational organization participation:ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CICA, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE (partner), Paris Club (associate), PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador AHN Ho-youngchancery: 2450 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 939-5600FAX: [1] (202) 797-0595consulate(s) general: Agana (Guam), Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Honolulu, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Seattleconsulate(s) general: Anchorage (AK)Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Sung Y. KIMembassy: 188 Sejong-daero, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-710mailing address: US Embassy Seoul, Unit 15550, APO AP 96205-5550telephone: [82] (2) 397-4200FAX: [82] (2) 725-0152Flag description:white with a red (top) and blue yin-yang symbol in the center; there is a different black trigram from the ancient I Ching (Book of Changes) in each corner of the white field; the Korean national flag is called Taegukki; white is a traditional Korean color and represents peace and purity; the blue section represents the negative cosmic forces of the yin, while the red symbolizes the opposite positive forces of the yang; each trigram (kwae) denotes one of the four universal elements, which together express the principle of movement and harmonyNational symbol(s):taegeuk (yin yang symbol)National anthem:name: ""Aegukga"" (Patriotic Song)lyrics/music: YUN Ch'i-Ho or AN Ch'ang-Ho/AHN Eaktaynote: adopted 1948, well known by 1910; both North Korea and South Korea's anthems share the same name and have a vaguely similar melody but have different lyricsEconomy ::Korea, SouthEconomy - overview:South Korea over the past four decades has demonstrated incredible growth and global integration to become a high-tech industrialized economy. In the 1960s, GDP per capita was comparable with levels in the poorer countries of Africa and Asia. In 2004, South Korea joined the trillion dollar club of world economies, and is currently the world's 12th largest economy. Initially, a system of close government and business ties, including directed credit and import restrictions, made this success possible. The government promoted the import of raw materials and technology at the expense of consumer goods, and encouraged savings and investment over consumption. The Asian financial crisis of 1997-98 exposed longstanding weaknesses in South Korea's development model including high debt/equity ratios and massive short-term foreign borrowing. GDP plunged by 6.9% in 1998, and then recovered by 9% in 1999-2000. Korea adopted numerous economic reforms following the crisis, including greater openness to foreign investment and imports. Growth moderated to about 4% annually between 2003 and 2007. Korea''s export focused economy was hit hard by the 2008 global economic downturn, but quickly rebounded in subsequent years, reaching 6.3% growth in 2010. The US-South Korea Free Trade Agreement was ratified by both governments in 2011 and went into effect in March 2012. Throughout 2012 the economy experienced sluggish growth because of market slowdowns in the United States, China, and the Eurozone. The incoming administration in 2013, following the December 2012 presidential election, is likely to face the challenges of balancing heavy reliance on exports with developing domestic-oriented sectors, such as services. The South Korean economy''s long term challenges include a rapidly aging population, inflexible labor market, and heavy reliance on exports - which comprise half of GDP.GDP (purchasing power parity):$1.64 trillion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13$1.608 trillion (2011 est.)$1.552 trillion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$1.156 trillion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1373.6% (2011 est.)6.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$32,800 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 43$32,300 (2011 est.)$31,400 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:31.4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2131.9% of GDP (2011 est.)32.4% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 53.5%government consumption: 15.8%investment in fixed capital: 26.7%investment in inventories: 0.8%exports of goods and services: 56.5%imports of goods and services: -53.4%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 2.7%industry: 39.8%services: 57.5% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:rice, root crops, barley, vegetables, fruit; cattle, pigs, chickens, milk, eggs; fishIndustries:electronics, telecommunications, automobile production, chemicals, shipbuilding, steelIndustrial production growth rate:1.7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 104Labor force:25.5 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 6.2%industry: 23.8%services: 70% (2012 est.)Unemployment rate:3.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 273.4% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:16.5% (2011 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 6.4%highest 10%: 37.7% (2011)Distribution of family income - Gini index:41.9 (2011)country comparison to the world: 5135.8 (2000)Budget:revenues: $276.5 billionexpenditures: $260.1 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:23.9% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):1.4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Public debt:36.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9536.2% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 504% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:1.5% (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 1311.25% (31 December 2009)Commercial bank prime lending rate:5.39% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1465.77% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$392 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 14$369.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$1.596 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 12$1.484 trillion (31 December 2011)Stock of domestic credit:$1.219 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16$1.098 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.024 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 15$994.3 billion (31 December 2011)$1.089 trillion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:$3.14 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34$26.51 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$552.6 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7$551.8 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:semiconductors, wireless telecommunications equipment, motor vehicles, computers, steel, ships, petrochemicalsExports - partners:China 24.4%, US 10.1%, Japan 7.1% (2011 est.)Imports:$514.2 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8$520.1 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery, electronics and electronic equipment, oil, steel, transport equipment, organic chemicals, plasticsImports - partners:China 16.5%, Japan 13%, US 8.5%, Saudi Arabia 7.1%, Australia 5% (2011 est.)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$327 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$306.4 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$413.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 28$398.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$138.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 32$133.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$327.5 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 19$190.4 billion (31 December 2011)Exchange rates:South Korean won (KRW) per US dollar -1,126.47 (2012 est.)1,108.29 (2011 est.)1,156.1 (2010 est.)1,276.93 (2009)1,101.7 (2008)Energy ::Korea, SouthElectricity - production:459.5 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Electricity - consumption:455.1 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2011)country comparison to the world: 214Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2011)country comparison to the world: 205Electricity - installed generating capacity:80.59 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 13Electricity - from fossil fuels:69.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Electricity - from nuclear fuels:22% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 135Electricity - from other renewable sources:1.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Crude oil - production:19,990 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 137Crude oil - imports:2.59 million bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Crude oil - proved reserves:NA bblRefined petroleum products - production:2.83 million bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Refined petroleum products - consumption:2.26 million bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10Refined petroleum products - exports:907,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Refined petroleum products - imports:753,900 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Natural gas - production:539.3 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Natural gas - consumption:45.9 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Natural gas - imports:46.83 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Natural gas - proved reserves:5.748 billion cu m (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:579 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Communications ::Korea, SouthTelephones - main lines in use:29.468 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 11Telephones - mobile cellular:52.507 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 27Telephone system:general assessment: excellent domestic and international services featuring rapid incorporation of new technologiesdomestic: fixed-line and mobile-cellular services widely available with a combined telephone subscribership of roughly 170 per 100 persons; rapid assimilation of a full range of telecommunications technologies leading to a boom in e-commerceinternational: country code - 82; numerous submarine cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations - 66 (2011)Broadcast media:multiple national TV networks with 2 of the 3 largest networks publicly operated; the largest privately owned network, Seoul Broadcasting Service (SBS), has ties with other commercial TV networks; cable and satellite TV subscription services available; publicly operated radio broadcast networks and many privately owned radio broadcasting networks, each with multiple affiliates, and independent local stations (2010)Internet country code:.krInternet hosts:315,697 (2012)country comparison to the world: 62Internet users:39.4 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 11Transportation ::Korea, SouthAirports:111 (2013)country comparison to the world: 53Airports - with paved runways:total: 71over 3,047 m: 42,438 to 3,047 m: 191,524 to 2,437 m: 12914 to 1,523 m: 13under 914 m: 23 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 40914 to 1,523 m: 2under 914 m:38 (2013)Heliports:466 (2013)Pipelines:gas 2,216 km; oil 16 km; refined products 889 km (2013)Railways:total: 3,381 kmcountry comparison to the world: 51standard gauge: 3,381 km 1.435-m gauge (1,843 km electrified) (2008)Roadways:total: 103,029 kmcountry comparison to the world: 42paved: 80,642 km (includes 3,367 km of expressways)unpaved: 22,387 km (2008)Waterways:1,600 km (most navigable only by small craft) (2011)country comparison to the world: 51Merchant marine:total: 786country comparison to the world: 14by type: bulk carrier 191, cargo 235, carrier 8, chemical tanker 130, container 72, liquefied gas 44, passenger 5, passenger/cargo 15, petroleum tanker 55, refrigerated cargo 15, roll on/roll off 10, vehicle carrier 6foreign-owned: 31 (China 6, France 2, Japan 14, Taiwan 1, US 8)registered in other countries: 457 (Bahamas 1, Cambodia 10, Ghana 1, Honduras 6, Hong Kong 3, Indonesia 2, Kiribati 1, Liberia 2, Malta 2, Marshall Islands 41, North Korea 1, Panama 373, Philippines 1, Russia 1, Singapore 3, Tuvalu 1, unknown 8) (2010)Ports and terminals:major ports: Incheon, Pohang, Busan, Ulsan, Yeosucontainer ports: Busan (16,163,842), Kwangyang (2,061,958), Incheon (1,924,644)Military ::Korea, SouthMilitary branches:Republic of Korea Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force (2011)Military service age and obligation:20-30 years of age for compulsory military service, with middle school education required; conscript service obligation - 21 months (Army, Marines), 23 months (Navy), 24 months (Air Force); 18-26 years of age for voluntary military service; women, in service since 1950, admitted to 7 service branches, including infantry, but excluded from artillery, armor, anti-air, and chaplaincy corps; HIV-positive individuals are exempt from military service (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 13,185,794females age 16-49: 12,423,496 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 10,864,566females age 16-49: 10,168,709 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 365,760female: 321,225 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:2.7% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 47Transnational Issues ::Korea, SouthDisputes - international:Military Demarcation Line within the 4-km-wide Demilitarized Zone has separated North from South Korea since 1953; periodic incidents with North Korea in the Yellow Sea over the Northern Limit Line, which South Korea claims as a maritime boundary; South Korea and Japan claim Liancourt Rocks (Tok-do/Take-shima), occupied by South Korea since 1954Refugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 179 (2012)"
Introduction ::Korea, SouthBackground:An independent kingdom for much of its long history, Korea was occupied by Japan beginning in 1905 following the Russo-Japanese War. In 1910, Tokyo formally annexed the entire Peninsula. Korea regained its independence following Japan's surrender to the United States in 1945. After World War II, a democratic-based government (Republic of Korea, ROK) was set up in the southern half of the Korean Peninsula while a communist-style government was installed in the north (Democratic People's Republic of Korea, DPRK). During the Korean War (1950-53), US troops and UN forces fought alongside ROK soldiers to defend South Korea from a DPRK invasion supported by China and the Soviet Union. A 1953 armistice split the peninsula along a demilitarized zone at about the 38th parallel. PARK Chung-hee took over leadership of the country in a 1961 coup. During his regime, from 1961 to 1979, South Korea achieved rapid economic growth, with per capita income rising to roughly 17 times the level of North Korea. South Korea held its first free presidential election under a revised democratic constitution in 1987, with former ROK Army general ROH Tae-woo winning a close race. In 1993, KIM Young-sam (1993-98) became South Korea's first civilian president. South Korea today is a fully functioning modern democracy. LEE Myung-bak (2008-2013) pursued a policy of global engagement , highlighted by Seoul's hosting of the G-20 summit in November 2010 and the Nuclear Security Summit in March 2012. South Korea also secured a non-permanent seat (2013-14) on the UN Security Council and will host the 2018 Winter Olympic Games. President PARK Geun-hye took office in February 2013 and is South Korea's first female leader. Serious tensions with North Korea have punctuated inter-Korean relations in recent years, including the North's sinking of the South Korean warship Cheonan in March 2010 and its artillery attack on South Korean soldiers and citizens in November 2010. In January 2013, South Korea assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2013-14 term.Geography ::Korea, SouthLocation:Eastern Asia, southern half of the Korean Peninsula bordering the Sea of Japan and the Yellow SeaGeographic coordinates:37 00 N, 127 30 EArea:total: 99,720 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 109land: 96,920 sq kmwater: 2,800 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than IndianaLand boundaries:total: 238 kmborder countries: North Korea 238 kmCoastline:2,413 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nm; between 3 nm and 12 nm in the Korea Straitcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: not specifiedClimate:temperate, with rainfall heavier in summer than winterTerrain:mostly hills and mountains; wide coastal plains in west and southElevation extremes:lowest point: Sea of Japan 0 mhighest point: Halla-san 1,950 mNatural resources:coal, tungsten, graphite, molybdenum, lead, hydropower potentialLand use:arable land: 14.93%permanent crops: 2.06%other: 83% (2011)Irrigated land:8,804 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:69.7 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 25.47 cu km/yr (26%/12%/62%)per capita: 548.7 cu m/yr (2003)Natural hazards:occasional typhoons bring high winds and floods; low-level seismic activity common in southwestvolcanism: Halla (elev. 1,950 m) is considered historically active although it has not erupted in many centuriesEnvironment - current issues:air pollution in large cities; acid rain; water pollution from the discharge of sewage and industrial effluents; drift net fishingEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:strategic location on Korea StraitPeople and Society ::Korea, SouthNationality:noun: Korean(s)adjective: KoreanEthnic groups:homogeneous (except for about 20,000 Chinese)Languages:Korean, English (widely taught in junior high and high school)Religions:Christian 31.6% (Protestant 24%, Roman Catholic 7.6%), Buddhist 24.2%, other or unknown 0.9%, none 43.3% (2010 survey)Population:48,955,203 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Age structure:0-14 years: 14.6% (male 3,717,701/female 3,424,490)15-24 years: 13.6% (male 3,525,050/female 3,117,198)25-54 years: 47.8% (male 11,925,181/female 11,491,841)55-64 years: 11.7% (male 2,842,996/female 2,907,730)65 years and over: 12.3% (male 2,469,093/female 3,533,923) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 37.1 %youth dependency ratio: 20.4 %elderly dependency ratio: 16.7 %potential support ratio: 6 (2013)Median age:total: 39.7 yearsmale: 38.2 yearsfemale: 41 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.18% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Birth rate:8.33 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 219Death rate:6.5 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Net migration rate:0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Urbanization:urban population: 83.2% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 0.71% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:SEOUL (capital) 9.778 million; Busan (Pusan) 3.439 million; Incheon (Inch'on) 2.572 million; Daegu (Taegu) 2.458 million; Daejon (Taejon) 1.497 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.09 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.13 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.04 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.69 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:29.6 (2008 est.)Maternal mortality rate:16 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 144Infant mortality rate:total: 4.01 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 200male: 4.21 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.79 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 79.55 yearscountry comparison to the world: 42male: 76.4 yearsfemale: 82.91 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.24 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 219Contraceptive prevalence rate:80%note: percent of women aged 15-44 (2009)Health expenditures:6.9% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 85Physicians density:1.97 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:10.3 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 88% of populationtotal: 98% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 12% of populationtotal: 2% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 142HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:9,500 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 100HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 500 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 85Obesity - adult prevalence rate:7.7% (2008)country comparison to the world: 139Education expenditures:5.1% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 74Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 97.9%male: 99.2%female: 96.6% (2002)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 yearsmale: 18 yearsfemale: 16 years (2010)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 9.6%country comparison to the world: 108male: 12.1%female: 8.1% (2011)Government ::Korea, SouthCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Koreaconventional short form: South Korealocal long form: Taehan-min'guklocal short form: Han'gukabbreviation: ROKGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Seoulgeographic coordinates: 37 33 N, 126 59 Etime difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:9 provinces (do, singular and plural), 6 metropolitan cities (gwangyoksi, singular and plural), 1 special city, and 1 special self-governing cityprovinces: Chungbuk (North Chungcheong), Chungnam (South Chungcheong), Gangwon, Gyeonggi, Gyeongbuk (North Gyeongsang), Gyeongnam (South Gyeongsang), Jeju, Jeonbuk (North Jeolla), Jeonnam (South Jeolla)metropolitan cities: Busan (Pusan), Daegu (Taegu), Daejon (Taejon), Gwangju (Kwangju), Incheon (Inch'on), Ulsanspecial city: Seoulspecial self-governing city: SejongIndependence:15 August 1945 (from Japan)National holiday:Liberation Day, 15 August (1945)Constitution:17 July 1948; note - amended or rewritten many times; current constitution approved 29 October 1987Legal system:mixed legal system combining European civil law, Anglo-American law, and Chinese classical thoughtInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:19 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President PARK Geun-hye (since 25 February 2013)head of government: Prime Minister CHUNG Hong-won (since 26 February 2013); Deputy Prime Minister HYUN Oh-seok (since 26 June 2013)cabinet: State Council appointed by the president on the prime minister's recommendation(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a single five-year term; PARK Geun-hye elected on 19 December 2012; next election to be held in December 2017; prime minister appointed by president with consent of National Assemblyelection results: PARK Geun-Hye elected president on 19 December 2012; percent of vote - PARK Geun-Hye (NFP) 51.6%, MOON Jae-In (DUP) 48%, others 0.4%Legislative branch:unicameral National Assembly or Gukhoe (300 seats; 246 members elected in single-seat constituencies, 54 elected by proportional representation; members serve four-year terms)elections: last held on 11 April 2012 (next to be held in April 2016)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NFP 152, DUP 127, UPP 13, LFP 5, independents 3Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of South Korea (consists of a chief justice and 13 justices); Constitutional Court (consists of a court head and 8 justices)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president with the consent of the National Assembly; other justices appointed by the president upon the recommendation of the chief justice and consent of the National Assembly; position of the chief justice is a 6-year non-renewable term; other justices serve 6-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court justices appointed - 3 by the president, 3 by the National Assembly, and 3 by the Supreme Court chief justice; court head serves until retirement at age 70, while other justices serve 6-year renewable terms with mandatory retirement at age 65subordinate courts: High Courts; District Courts; Branch Courts (organized undeer the Branch Courts); specialized courts for family and administrative issuesPolitical parties and leaders:Democratic Party or DP (formerly the Democratic United Party or DUP) [KIM Han-gil]Liberty Forward Party or LFP (now part of the NFP)New Frontier Party (NFP) or Saenuri (formerly Grand National Party) [HWANG Woo-yea]Progressive Justice Party or PJP [ROH Hoe-chan and CHO Joon-ho]United Progressive Party or UPP [LEE Jung-hee]Political pressure groups and leaders:Catholic Priests' Association for JusticeCitizen's Coalition for Economic JusticeFederation of Korean IndustriesFederation of Korean Trade UnionsKorean Confederation of Trade UnionsKorean Veterans' AssociationLawyers for a Democratic SocietyNational Council of ChurchesPeople's Solidarity for Participatory DemocracyInternational organization participation:ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CICA, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE (partner), Paris Club (associate), PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador AHN Ho-youngchancery: 2450 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 939-5600FAX: [1] (202) 797-0595consulate(s) general: Agana (Guam), Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Honolulu, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Seattleconsulate(s) general: Anchorage (AK)Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Sung Y. KIMembassy: 188 Sejong-daero, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-710mailing address: US Embassy Seoul, Unit 15550, APO AP 96205-5550telephone: [82] (2) 397-4200FAX: [82] (2) 725-0152Flag description:white with a red (top) and blue yin-yang symbol in the center; there is a different black trigram from the ancient I Ching (Book of Changes) in each corner of the white field; the Korean national flag is called Taegukki; white is a traditional Korean color and represents peace and purity; the blue section represents the negative cosmic forces of the yin, while the red symbolizes the opposite positive forces of the yang; each trigram (kwae) denotes one of the four universal elements, which together express the principle of movement and harmonyNational symbol(s):taegeuk (yin yang symbol)National anthem:name: ""Aegukga"" (Patriotic Song)lyrics/music: YUN Ch'i-Ho or AN Ch'ang-Ho/AHN Eaktaynote: adopted 1948, well known by 1910; both North Korea and South Korea's anthems share the same name and have a vaguely similar melody but have different lyricsEconomy ::Korea, SouthEconomy - overview:South Korea over the past four decades has demonstrated incredible growth and global integration to become a high-tech industrialized economy. In the 1960s, GDP per capita was comparable with levels in the poorer countries of Africa and Asia. In 2004, South Korea joined the trillion dollar club of world economies, and is currently the world's 12th largest economy. Initially, a system of close government and business ties, including directed credit and import restrictions, made this success possible. The government promoted the import of raw materials and technology at the expense of consumer goods, and encouraged savings and investment over consumption. The Asian financial crisis of 1997-98 exposed longstanding weaknesses in South Korea's development model including high debt/equity ratios and massive short-term foreign borrowing. GDP plunged by 6.9% in 1998, and then recovered by 9% in 1999-2000. Korea adopted numerous economic reforms following the crisis, including greater openness to foreign investment and imports. Growth moderated to about 4% annually between 2003 and 2007. Korea''s export focused economy was hit hard by the 2008 global economic downturn, but quickly rebounded in subsequent years, reaching 6.3% growth in 2010. The US-South Korea Free Trade Agreement was ratified by both governments in 2011 and went into effect in March 2012. Throughout 2012 the economy experienced sluggish growth because of market slowdowns in the United States, China, and the Eurozone. The incoming administration in 2013, following the December 2012 presidential election, is likely to face the challenges of balancing heavy reliance on exports with developing domestic-oriented sectors, such as services. The South Korean economy''s long term challenges include a rapidly aging population, inflexible labor market, and heavy reliance on exports - which comprise half of GDP.GDP (purchasing power parity):$1.64 trillion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13$1.608 trillion (2011 est.)$1.552 trillion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$1.156 trillion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1373.6% (2011 est.)6.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$32,800 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 43$32,300 (2011 est.)$31,400 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:31.4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2131.9% of GDP (2011 est.)32.4% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 53.5%government consumption: 15.8%investment in fixed capital: 26.7%investment in inventories: 0.8%exports of goods and services: 56.5%imports of goods and services: -53.4%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 2.7%industry: 39.8%services: 57.5% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:rice, root crops, barley, vegetables, fruit; cattle, pigs, chickens, milk, eggs; fishIndustries:electronics, telecommunications, automobile production, chemicals, shipbuilding, steelIndustrial production growth rate:1.7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 104Labor force:25.5 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 6.2%industry: 23.8%services: 70% (2012 est.)Unemployment rate:3.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 273.4% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:16.5% (2011 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 6.4%highest 10%: 37.7% (2011)Distribution of family income - Gini index:41.9 (2011)country comparison to the world: 5135.8 (2000)Budget:revenues: $276.5 billionexpenditures: $260.1 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:23.9% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):1.4% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Public debt:36.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9536.2% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 504% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:1.5% (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 1311.25% (31 December 2009)Commercial bank prime lending rate:5.39% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1465.77% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$392 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 14$369.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$1.596 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 12$1.484 trillion (31 December 2011)Stock of domestic credit:$1.219 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16$1.098 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.024 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 15$994.3 billion (31 December 2011)$1.089 trillion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:$3.14 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34$26.51 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$552.6 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7$551.8 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:semiconductors, wireless telecommunications equipment, motor vehicles, computers, steel, ships, petrochemicalsExports - partners:China 24.4%, US 10.1%, Japan 7.1% (2011 est.)Imports:$514.2 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8$520.1 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery, electronics and electronic equipment, oil, steel, transport equipment, organic chemicals, plasticsImports - partners:China 16.5%, Japan 13%, US 8.5%, Saudi Arabia 7.1%, Australia 5% (2011 est.)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$327 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$306.4 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$413.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 28$398.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$138.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 32$133.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$327.5 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 19$190.4 billion (31 December 2011)Exchange rates:South Korean won (KRW) per US dollar -1,126.47 (2012 est.)1,108.29 (2011 est.)1,156.1 (2010 est.)1,276.93 (2009)1,101.7 (2008)Energy ::Korea, SouthElectricity - production:459.5 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Electricity - consumption:455.1 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2011)country comparison to the world: 214Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2011)country comparison to the world: 205Electricity - installed generating capacity:80.59 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 13Electricity - from fossil fuels:69.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Electricity - from nuclear fuels:22% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 135Electricity - from other renewable sources:1.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Crude oil - production:19,990 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 137Crude oil - imports:2.59 million bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Crude oil - proved reserves:NA bblRefined petroleum products - production:2.83 million bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Refined petroleum products - consumption:2.26 million bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10Refined petroleum products - exports:907,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Refined petroleum products - imports:753,900 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Natural gas - production:539.3 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Natural gas - consumption:45.9 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Natural gas - imports:46.83 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Natural gas - proved reserves:5.748 billion cu m (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:579 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Communications ::Korea, SouthTelephones - main lines in use:29.468 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 11Telephones - mobile cellular:52.507 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 27Telephone system:general assessment: excellent domestic and international services featuring rapid incorporation of new technologiesdomestic: fixed-line and mobile-cellular services widely available with a combined telephone subscribership of roughly 170 per 100 persons; rapid assimilation of a full range of telecommunications technologies leading to a boom in e-commerceinternational: country code - 82; numerous submarine cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations - 66 (2011)Broadcast media:multiple national TV networks with 2 of the 3 largest networks publicly operated; the largest privately owned network, Seoul Broadcasting Service (SBS), has ties with other commercial TV networks; cable and satellite TV subscription services available; publicly operated radio broadcast networks and many privately owned radio broadcasting networks, each with multiple affiliates, and independent local stations (2010)Internet country code:.krInternet hosts:315,697 (2012)country comparison to the world: 62Internet users:39.4 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 11Transportation ::Korea, SouthAirports:111 (2013)country comparison to the world: 53Airports - with paved runways:total: 71over 3,047 m: 42,438 to 3,047 m: 191,524 to 2,437 m: 12914 to 1,523 m: 13under 914 m: 23 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 40914 to 1,523 m: 2under 914 m:38 (2013)Heliports:466 (2013)Pipelines:gas 2,216 km; oil 16 km; refined products 889 km (2013)Railways:total: 3,381 kmcountry comparison to the world: 51standard gauge: 3,381 km 1.435-m gauge (1,843 km electrified) (2008)Roadways:total: 103,029 kmcountry comparison to the world: 42paved: 80,642 km (includes 3,367 km of expressways)unpaved: 22,387 km (2008)Waterways:1,600 km (most navigable only by small craft) (2011)country comparison to the world: 51Merchant marine:total: 786country comparison to the world: 14by type: bulk carrier 191, cargo 235, carrier 8, chemical tanker 130, container 72, liquefied gas 44, passenger 5, passenger/cargo 15, petroleum tanker 55, refrigerated cargo 15, roll on/roll off 10, vehicle carrier 6foreign-owned: 31 (China 6, France 2, Japan 14, Taiwan 1, US 8)registered in other countries: 457 (Bahamas 1, Cambodia 10, Ghana 1, Honduras 6, Hong Kong 3, Indonesia 2, Kiribati 1, Liberia 2, Malta 2, Marshall Islands 41, North Korea 1, Panama 373, Philippines 1, Russia 1, Singapore 3, Tuvalu 1, unknown 8) (2010)Ports and terminals:major ports: Incheon, Pohang, Busan, Ulsan, Yeosucontainer ports: Busan (16,163,842), Kwangyang (2,061,958), Incheon (1,924,644)Military ::Korea, SouthMilitary branches:Republic of Korea Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force (2011)Military service age and obligation:20-30 years of age for compulsory military service, with middle school education required; conscript service obligation - 21 months (Army, Marines), 23 months (Navy), 24 months (Air Force); 18-26 years of age for voluntary military service; women, in service since 1950, admitted to 7 service branches, including infantry, but excluded from artillery, armor, anti-air, and chaplaincy corps; HIV-positive individuals are exempt from military service (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 13,185,794females age 16-49: 12,423,496 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 10,864,566females age 16-49: 10,168,709 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 365,760female: 321,225 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:2.7% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 47Transnational Issues ::Korea, SouthDisputes - international:Military Demarcation Line within the 4-km-wide Demilitarized Zone has separated North from South Korea since 1953; periodic incidents with North Korea in the Yellow Sea over the Northern Limit Line, which South Korea claims as a maritime boundary; South Korea and Japan claim Liancourt Rocks (Tok-do/Take-shima), occupied by South Korea since 1954Refugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 179 (2012)"
The World Factbook. 2014.
